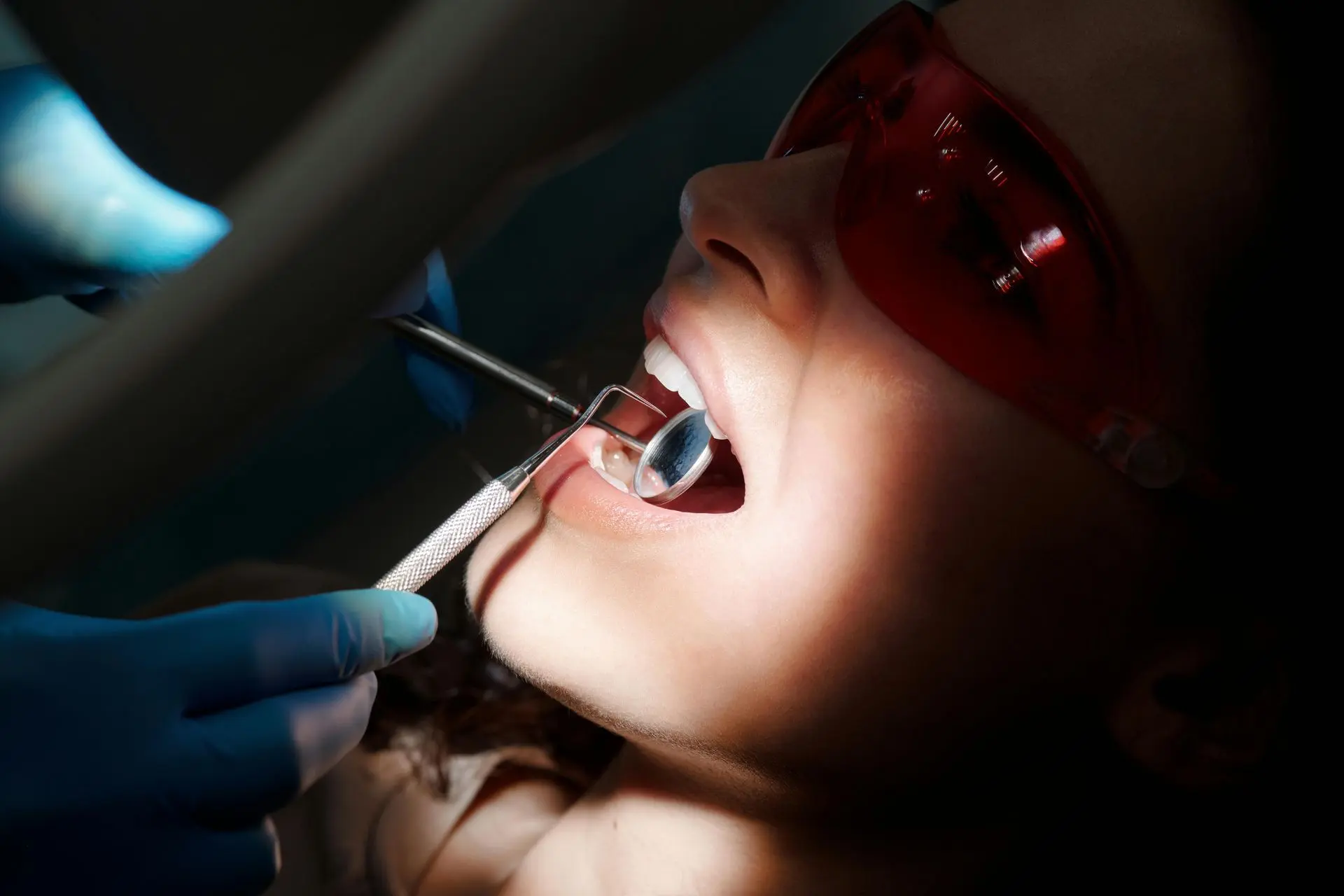
Thanks to the use of lasers in dentistry, without pain and without the need for local anesthesia, it is possible to treat all cavities as well as perform minor surgeries in the maximum comfort of the patient.
Laser therapy treatments are shorter and involve less bleeding of the treated area. Laser therapy also results in significantly less pain during and after treatments and less invasive treatment.
All lasers work by delivering energy in the form of light. When used for surgical and dental procedures, the laser acts as a cutting instrument or a vaporizer of tissue that it comes into contact with. When used in teeth-whitening procedures, the laser acts as a heat source and enhances the effect of tooth-bleaching agents.
Dentistry

Thanks to the use of lasers in dentistry, without pain and without the need for local anesthesia, it is possible to treat all cavities as well as perform minor surgeries in the maximum comfort of the patient.
Laser therapy treatments are shorter and involve less bleeding of the treated area. Laser therapy also results in significantly less pain during and after treatments and less invasive treatment.
All lasers work by delivering energy in the form of light. When used for surgical and dental procedures, the laser acts as a cutting instrument or a vaporizer of tissue that it comes into contact with. When used in teeth-whitening procedures, the laser acts as a heat source and enhances the effect of tooth-bleaching agents.
Dentistry
In dentistry, lasers are used for a variety of procedures involving both hard and soft tissues, offering precision, reduced pain, and faster healing. The most commonly used lasers in dental applications include diode lasers, CO₂ lasers, Er:YAG lasers, and Nd:YAG lasers, each selected based on the type of tissue and treatment required.
Diode lasers are widely used for soft tissue procedures such as gum reshaping, periodontal therapy, and lesion removal. They offer excellent cutting and coagulation with minimal bleeding, making them popular in routine dental surgeries.
CO₂ lasers are effective for soft tissue surgery as well, providing precise cutting with strong hemostasis and minimal thermal damage. They are often used in procedures like frenectomies and soft tissue biopsies.
Er:YAG lasers are ideal for hard tissue treatments, including cavity preparation, enamel etching, and bone surgery. Their ability to gently ablate tooth structure with minimal heat makes them especially useful in conservative dentistry and pediatric treatments.
Nd:YAG lasers are primarily used in periodontal therapy, especially for deep tissue decontamination and treating gum infections. They penetrate deeper into tissues and are effective for reducing bacteria and promoting healing.
The choice of laser in dentistry depends on the procedure type and tissue involved. Diode and CO₂ lasers are preferred for soft tissue applications, Er:YAG lasers for hard tissues, and Nd:YAG lasers for periodontal and deep tissue treatments.
In dentistry, lasers are used for a variety of procedures involving both hard and soft tissues, offering precision, reduced pain, and faster healing. The most commonly used lasers in dental applications include diode lasers, CO₂ lasers, Er:YAG lasers, and Nd:YAG lasers, each selected based on the type of tissue and treatment required.
Diode lasers are widely used for soft tissue procedures such as gum reshaping, periodontal therapy, and lesion removal. They offer excellent cutting and coagulation with minimal bleeding, making them popular in routine dental surgeries.
CO₂ lasers are effective for soft tissue surgery as well, providing precise cutting with strong hemostasis and minimal thermal damage. They are often used in procedures like frenectomies and soft tissue biopsies.
Er:YAG lasers are ideal for hard tissue treatments, including cavity preparation, enamel etching, and bone surgery. Their ability to gently ablate tooth structure with minimal heat makes them especially useful in conservative dentistry and pediatric treatments.
Nd:YAG lasers are primarily used in periodontal therapy, especially for deep tissue decontamination and treating gum infections. They penetrate deeper into tissues and are effective for reducing bacteria and promoting healing.
The choice of laser in dentistry depends on the procedure type and tissue involved. Diode and CO₂ lasers are preferred for soft tissue applications, Er:YAG lasers for hard tissues, and Nd:YAG lasers for periodontal and deep tissue treatments.




